含能粘合剂是指含有硝酸酯基(—ONO2)、硝基(—NO2)、硝胺基(—NNO2)、叠氮基(—N3)、二氟胺基(—NF2)等含能基团的粘合剂[1-2]。在含能粘合剂中, 由于叠氮类含能粘合剂具有放热量大、分解时不需要耗氧、分解产物分子量低、与硝胺类炸药有良好的相容性等优点, 引起了人们广泛地关注[3-5]。目前有应用价值的叠氮类粘合剂主要包括叠氮缩水甘油醚(GAP)、3, 3′-双叠氮甲基环氧丁烷(BAMO)、3-叠氮甲基-3′ -甲基环氧丁烷(AMMO)的均聚物及共聚物等。其中, 聚(3, 3′-二叠氮甲基环氧丁烷/3-叠氮甲基-3′-甲基环氧丁烷)(P(BAMO/AMMO))含能粘合剂具有较高的能量水平、良好的力学性能以及加工性能, 被喻为下一代固体推进剂和发射药首选含能粘合剂[6]。
热塑性弹性体基推进剂具有良好的加工性能和优异的力学性能, 可回收和重复利用, 是一种绿色环保型推进剂[7]。P(BAMO/AMMO)基推进剂正是这类推进剂典型代表, 目前对于P(BAMO/AMMO)基推进剂的研究主要是涉及P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的合成、表征[8-12]以及自身热分解性能[13-17]等。燃烧性能是评价固体推进剂的一项重要指标, 而为了实现P(BAMO/AMMO)推进剂的高速、稳定燃烧, 最方便、有效的方法就是添加燃速催化剂。研究表明推进剂组分的热分解性能与推进剂的燃烧性能密切相关[18], 因此研究燃速催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)基推进剂的主要组分P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂热分解性能的影响十分必要。目前针对燃速催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)基推进剂的固体组分如黑索今(RDX)、高氯酸铵(AP)等影响研究较多, Oyumi[19]研究了催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)/AN/HMX推进剂的热分解和燃烧特性, 研究表明重铬酸铵与铬酸铜联用是P(BAMO/AMMO)/AN/HMX推进剂最为有效的燃速调节剂, 可显著提高推进剂的燃速并降低推进剂的压力指数。而有关燃速催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂自身热分解性能的影响研究尚未见报道, 故本工作主要采用差示扫描量热法(DSC)和热重分析(TG)研究固体火箭推进剂中几种常用的燃速催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂热分解性能的影响。
2 实验部分 2.1 试剂与仪器CuO:化学纯,天津博迪化工股份有限公司; Fe2O3:化学纯,天津市登科化学试剂有限公司; 碳黑(CB):化学纯,宏源化工原料有限公司; PbCO3:化学纯,天津市光复精细化工研究所; Bi2O3:化学纯,宏源化工原料有限公司; (NH4)2Cr2O7:化学纯,成都格雷西亚化学技术有限公司; 1, 4-丁二醇(BDO):分析纯, 北京化工厂; 甲苯二异氰酸酯(TDI), 分析纯, 北京化学试剂厂; P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂:实验室自制[20], 相对分子质量31000, 其中PBAMO与PAMMO的质量比为1:1, 硬段(BDO+TDI)含量为20%;
采用差示扫描量热法(DSC, 日本津岛公司DSC-60)对样品进行热分解测试, 铝坩埚, 试样量小于2 mg, 动态气氛为高纯氮气, 流量为50 mL·min-1, 升温速率10 ℃·min-1; 采用热重(TG, METTLER TOLEDO TGA/DSC同步热分析仪)对样品进行热失重分析, 氧化铝坩埚, 试样量小于2 mg, 动态气氛为高纯氮气, 升温速率10 ℃·min-1。
2.2 实验过程准确称量10 g P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂于烧瓶中, 加入100 mL二氯甲烷, 磁力搅拌使其完全溶解, 准确称量0.5 g燃速催化剂(CuO、Fe2O3、CB、PbCO3、Bi2O3、(NH4)2Cr2O7)于烧瓶中, 继续搅拌30 min, 将烧瓶置于超声水浴中分散30 min, 减压蒸馏除去溶剂, 得到P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂与燃速催化剂(CuO、Fe2O3、CB、PbCO3、Bi2O3、(NH4)2Cr2O7)的混合物, 置于真空干燥箱内, 60 ℃下真空干燥4 h即可制得样品。
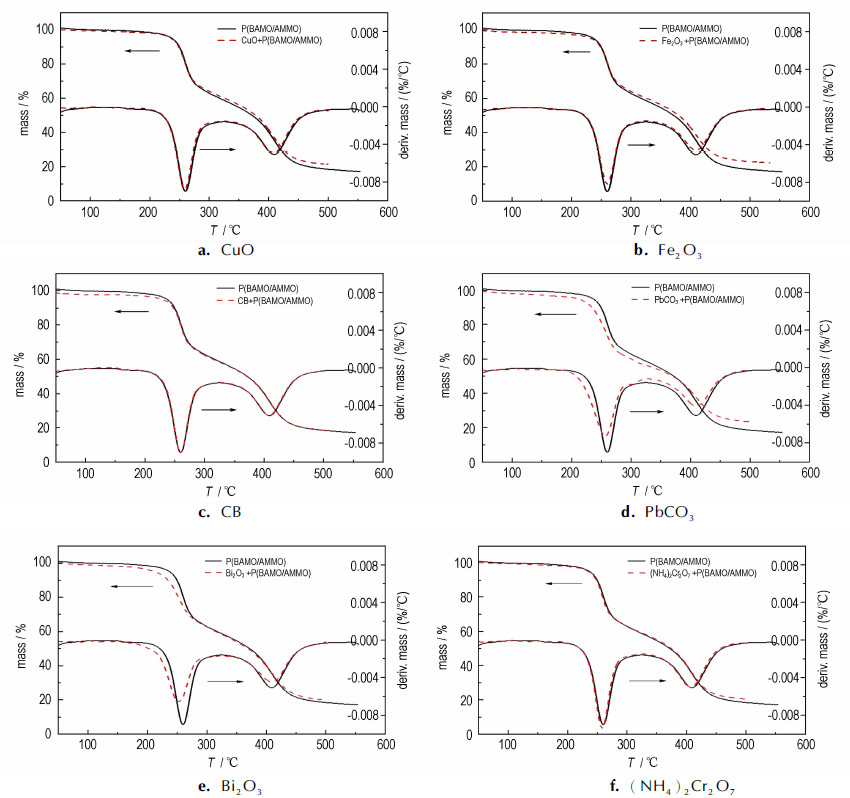
3 结果与讨论 3.1 TG分析催化剂/P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂样品的TG-DTG曲线如图 1所示,升温区间50~500 ℃, 每组样品都有两个失重阶段, 各自的TG-DTG特性量列于表 1中。
|
图 1 6种燃速催化剂/P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的TG-DTG曲线 Fig.1 TG-DTG curves for six burning rate catalysts/P(BAMO/AMMO) |
| 表 1 不同样品的TG-DTG特征量 Tab.1 TG-DTG data of different samples |
如图 1所示, P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的TG曲线出现了两个失重阶段:第一个失重阶段出现在220~280 ℃, 失重质量分数为34%, 与粘合剂中叠氮基团的质量分数(33.2%)一致, 因此第一个失重阶段归属于侧链叠氮基团的热分解过程; 第二个失重阶段出现在280~500 ℃, 归属于预聚物聚醚主链的分解以及TDI与BDO所构成的聚氨酯硬段的分解, 之后质量趋于恒定。在DTG曲线中可以观察到2个失重分解峰, 与TG曲线相对应。由分解峰峰值确定两个分解过程最大失重速率峰分别在259.8, 409.0 ℃。
CuO、Fe2O3、CB、PbCO3、Bi2O3、(NH4)2Cr2O7与P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂组成的混合样品的TG曲线也出现了两个阶段, 失重阶段出现的温度范围与P(BAMO/AMMO)的热失重曲线类似, 都在220~280 ℃之间, 出现第一个失重阶段, 在280~500 ℃之间, 出现第二个失重阶段, 之后质量趋于恒定。由此可以看出, 6种燃速催化剂的加入并没有改变P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的热分解历程, 都在260 ℃左右和409 ℃左右出现峰。这表明含能材料的起始分解温度与推进剂的燃速密切相关, 而且起始分解温度是表征含能材料热分解特性的重要参数, 起始分解温度低、放热早, 能够提前为后续的热分解提供能量, 加快后续热分解反应的进行[18, 21-22]。由表 1可以看出, 6种催化剂都使P(BAMO/AMMO)的起始分解温度提前, CB、PbCO3使P(BAMO/AMMO)的起始分解温度分别提前了8.3, 24.2 ℃。220~280 ℃失重阶段对应的是P(BAMO/AMMO)的侧链叠氮基团的热分解, 可以看出以上6种催化剂均可以使叠氮基团的热分解温度提前, 而叠氮基团的分解放热提前可以加速粘合剂热分解, 因此, 以上6种燃速催化剂均可以有效催化粘合剂的热分解, CB、PbCO3的催化效果更优。
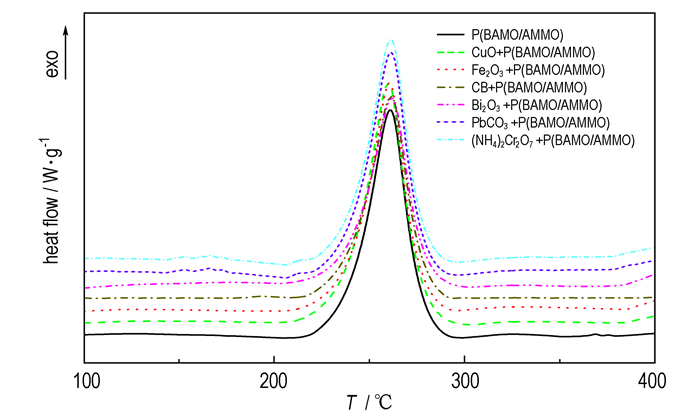
3.2 DSC分析由TG结果可知, 6种燃速催化剂的加入均使粘合剂的起始分解温度提前, 为进一步探讨这几种催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的热分解的影响, 对6种样品进行了DSC测试, 结果如图 2所示, 各样品的DSC特性量列于表 2。由P(BAMO/AMMO)的DSC曲线可以看出, P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的最大放热速率峰出现在260.8 ℃, 这与TG-DTG的结果一致, 而且催化剂的加入对叠氮基团的最大分解放热峰没有明显的影响, 都在260 ℃左右。
|
图 2 6种燃速催化剂/P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的DSC曲线 Fig.2 DSC curves for six burning rate catalysts/P(BAMO/AMMO) |
| 表 2 不同样品的DSC特征量 Tab.2 DSC data of different samples |
由表 2可知, P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的表观分解热ΔH为1.12 kJ·g-1, 燃速催化剂的加入对叠氮基团的表观分解热影响不同, 其中CuO、Fe2O3、PbCO3、(NH4)2Cr2O7的加入使叠氮基团的表观分解热分别增加了0.05, 0.09, 0.10, 0.06 kJ·g-1, 而CB、Bi2O3的加入则使得叠氮基团的表观分解热减少。叠氮基团的表观分解热越大, 放热越多, 为粘合剂的进一步分解提供的能量越多, 因此越有利于粘合剂的热分解。由此可知, CuO、Fe2O3、PbCO3、(NH4)2Cr2O7 4种燃速催化剂能有效催化P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的热分解。结合之前的TG结果可知, 6种燃速催化剂均使得P(BAMO/AMMO)的起始分解温度提前, 但是其中CB、Bi2O3的加入使P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的表观分解热减少, 因此, CuO、Fe2O3、PbCO3、(NH4)2Cr2O7为比较理想的P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的燃速催化剂。
4 结论热重分析结果表明, CuO、Fe2O3、CB、PbCO3、Bi2O3、(NH4)2Cr2O76种催化剂都使得P(BAMO/AMMO)的起始分解温度提前, CB、PbCO3的加入提前幅度较大, 这说明这几种催化剂都对P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的热分解起到了催化作用。DSC结果表明, CuO、Fe2O3、PbCO3、(NH4)2Cr2O7的加入使得P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的表观分解热, 分别增加了0.05, 0.09, 0.10,0.06 kJ·g-1, 而CB、Bi2O3的加入使得P(BAMO/AMMO)中叠氮基团的表观分解热减少, 不利于热分解反应的进行。因此, 综合TG与DSC结果可知, CuO、Fe2O3、PbCO3、(NH4)2Cr2O7更能有效地催化P(BAMO/AMMO)粘合剂的热分解放热反应。
| [1] |
陈支厦, 郑邯勇, 王树峰, 等. 叠氮类含能粘合剂研究进展[J].
舰船防化, 2007(2): 1-5. CHEN Zhi-xia, ZHENG Han-yong, WANG Shu-feng, et al. Status and advance of azide energetic binders[J]. Chemical Defence On Ships, 2007(2): 1-5. |
| [2] |
Talawar M B, Sivabalan R, Mukundan T, et al. Environmentally compatible next generation green energetic materials (GEMs)[J].
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161: 589-607. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.011 |
| [3] |
Sun Y L, Li S F. The Effect of nitrate esters on the thermal decomposition mechanism of GAP[J].
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 154: 112-117. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.002 |
| [4] |
Oyumi Y. Thermal decomposition of AMMO/AP Composite propellants[J].
Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 1993, 18: 168-172. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4087 |
| [5] |
Oyumi Y, Mitarai Y, Anan T. Mechanism of catalytic effects on AMMO/HMX composite propellants combustion rates[J].
Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 1993, 18: 195-200. DOI:10.1002/prep.v18:4 |
| [6] |
罗运军, 王晓青, 葛震.
含能聚合物[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011: 180-185.
LUO Yun-jun, WANG Xiao-qing, GE Zhen. Energetic Polymers[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, Beijing, 2011: 180-185. |
| [7] |
Mulage K S, Mishra A K, et al. Effect of ballistic modifiers on the burn rate of extruded composite propellant formulations based on thermoplastic elastomeric binder[J].
International Journal of Energetic Materials and Chemical Propulsion, 2012, 11(4): 375-388. DOI:10.1615/IntJEnergeticMaterialsChemProp.v11.i4 |
| [8] |
Piraino S, Kaste P, Snyder J, et al. Chemical and structural characterization of energetic thermoplastic elastomers: BAMO/AMMO Copolymers[C]//35th International Annual Conference of ICT, Karlsruhe: Institut Chemische Technologie, 2004.
|
| [9] |
Sanderson A J, Edwards W W. Method for the synthesis of energetic thermoplastic elastomers in non-halogenate solvents: US, 6997997[P], 2006.
|
| [10] |
Manser G E, Miller R S. Thermoplastic elastomers having alternate crystalline structure for as high energy binders: US, 5210153[P], 1993.
|
| [11] |
Barbieri U, Keicher T, Polacco G. Homo-and copolymers of 3-tosyloxymethyl-3-methyl oxetane (TMMO) as precursors to energetic azido polymers[J].
E-Polymers, 2009, 46: 1-11. |
| [12] |
Xu B P, Lillya C P, Chien J C W. Spiro(benzoxasilole) catalyzed polymerization of oxetane derivatives[J].
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 1992, 30: 1899-1909. DOI:10.1002/pola.1992.080300912 |
| [13] |
Zenin A A. Physics of combustion of new oxidizer/polymer mixtures[R]. AD-A420008, 2003.
|
| [14] |
Sell T, Vyazovkin S, Wight C A. Thermal decomposition kinetics of PBAN-binder and composite solid rocket propellants[J].
Combustion and Flame, 1999, 119: 174-181. DOI:10.1016/S0010-2180(99)00036-X |
| [15] |
Lee Y J, Kudva G, Litzinger T A. Thermal decomposition of BAMO/AMMO copolymer[R]. AIAA-2225, 1999.
|
| [16] |
Lee Y J, Litzinger T A. Thermal decomposition of BAMO/AMMO with and without TiO2[J].
Thermochimica Acta, 2002, 384: 121-135. DOI:10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00785-7 |
| [17] |
宋秀铎, 赵凤起, 王江宁, 等. BAMO-AMMO的热行为及其与含能组分的相容性[J].
火炸药学报, 2008, 31(3): 75-78. SONG Xiu-duo, ZHAO Feng-qi, WANG Jiang-ning, et al. Thermal behaviors of BAMO-AMMO and its compatibility with some energetic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2008, 31(3): 75-78. |
| [18] |
顾健, 吴京汉. 燃速催化剂LBC对GAP推进剂主要组分热分解行为的影响[J].
固体火箭技术, 2011, 34(4): 492-496. GU Jian, WU Jing-han. Effect of lead-salt burning-rate catalyst LBC on thermal decomposition behaviors of key constituents of GAP propellant[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2011, 34: 492-496. |
| [19] |
Oyumi Y, Inokami K, Yamazaki K, et al. Burning rate augmentation of BAMO based propellants[J].
Propellants, Explos, Pyrotech, 1994, 19: 180 DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4087 |
| [20] |
张弛. BAMO-AMMO含能粘合剂的合成、表征及应用研究[D]. 北京理工大学. 2011: 148-155.
ZHANG Chi. Synthesis, Characterization and application of BAMO-AMMO energetic binder[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2011: 148-155. |
| [21] |
Liu L L, Li FS, Tan LH, et al. Effects of Ni, Cu, A1 and Ni-Cu nanopowders on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J].
Propellants, Explosives, Pytechnics, 2004, 29(1): 34-38. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4087 |
| [22] |
陈伟凡, 李凤生, 刘建勋, 等. 纳米Co3O4的制备及其对高氯酸铵热分解的催化性能[J].
催化学报, 2005, 20(12): 1073-1077. CHEN Wei-fan, LI Feng-sheng, LIU Jian-xun, et al. Preparation of nanocrystalline Co3O4 and its catalytic performance for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2005, 20(12): 1073-1077. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9837.2005.12.008 |

Effects of CuO, Fe2O3, CB, PbCO3, Bi2O3 and (NH4)2Cr2O7 on the thermal decomposition properties of P(BAMO/AMMO) energetic binder were studied by TG and DSC.




